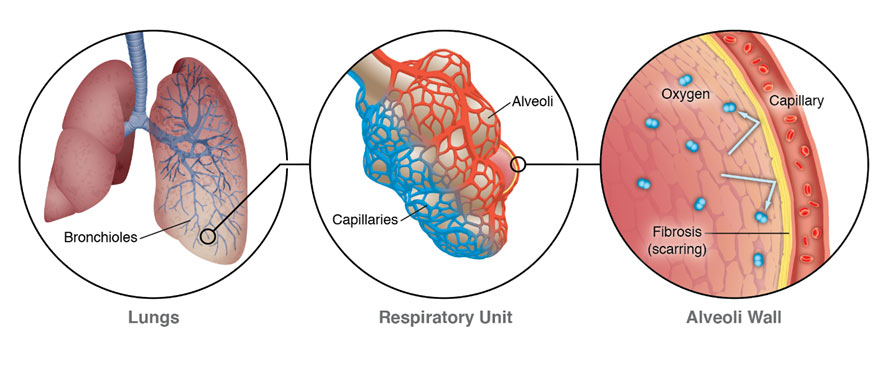
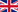
The interstitial tissue in the lung is located between the alveoli, and is affected by a variety of conditions, known or unknown.
Drugs, rheumatic diseases, infections, vascular diseases, occupational diseases, heart failure, cancerous lymphatic spread are some of the known causes of interstitial lung disease.
A condition of unknown aetiology may include pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, cryptogenic organized pneumonia, respiratory bronchiolitis of smokers, lymphangiolymomyomatosis (involving women of childbearing age), hystiocytosis X (involving young male smokers) and many others with different involvement.
The deep knowledge of the diagnostic approach of such diseases with medical history, high-resolution CT, bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage and transbronchial biopsies is the key to reveal them. The role of respiratory function tests is very important to monitor and assess the response of the disease to available treatments.