The role of the immune system is to protect us against any foreign material that can enter our body, e.g. virus, germ, pathogens, etc. In an autoimmune diseases the immune system does exactly the opposite and for some unknown reason it turns against the body.
Many of these diseases also affect the lungs. It is very important to recognize the pulmonary involvement and the disease and treat them appropriately.
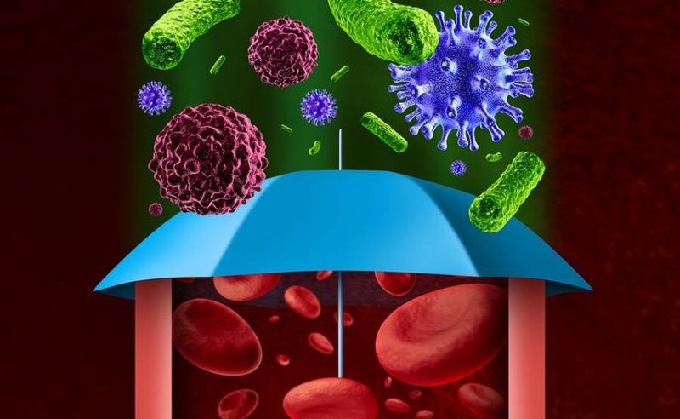
Systemic lupus erythematous
There are two common forms of lupus: dermal and systemic. Dermal lupus is a disease that is restricted to the skin, is chronic and leads to scarring. Systemic lupus can not only affect the joints and muscles, but also the skin, kidneys, nervous system, heart and lungs.
The most common pulmonary involvement is recurrent respiratory infections followed by fluid collection in the lung, pulmonary embolism, alveolar haemorrhage,lupus pneumonitis and many more.
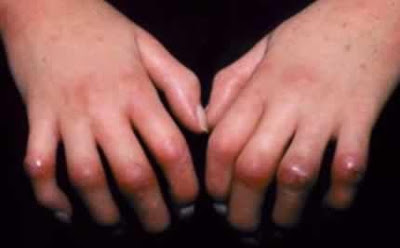
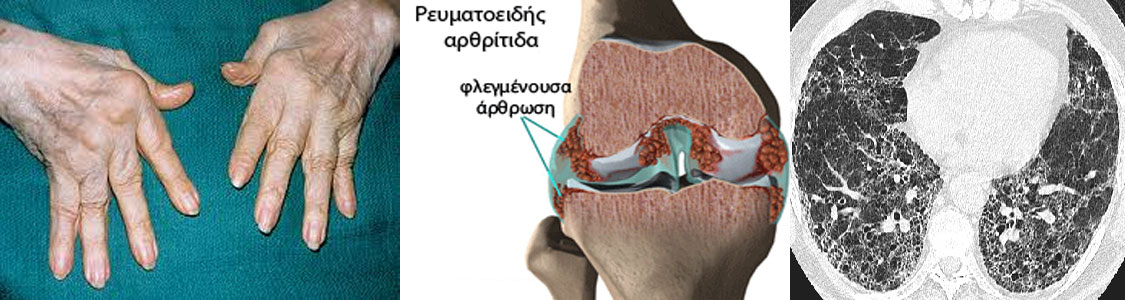
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, symmetric, polyarthritic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the synovial membrane of small joints. It can cause the deformation of the joints which may also cause chronic disability. This could also be accompanied by extra-articular manifestations and the most commonly found in the lung is fibrosis.
Scleroderma
Scleroderma or Systemic Sclerosis is a chronic, autoimmune disease of the connective tissue where the symptoms vary significantly from person to person.
Scleroderma develops with thickening of the skin, which becomes stiffer, loses its elasticity, becomes shiny and changes its color. In the diffuse form, the skin completely loses its elasticity, becomes stiffer, and extends to both hands, face and torso, while in the limited form it is restricted to the hands and the face.
The most common manifestation in the lung is fibrosis, followed by pulmonary hypertension.